This week, our journey in the ncRNAs universe brings us into the very heart of the cell, in its nucleus! With a view on the cytoplasm…
Let’s get going fellow travellers!
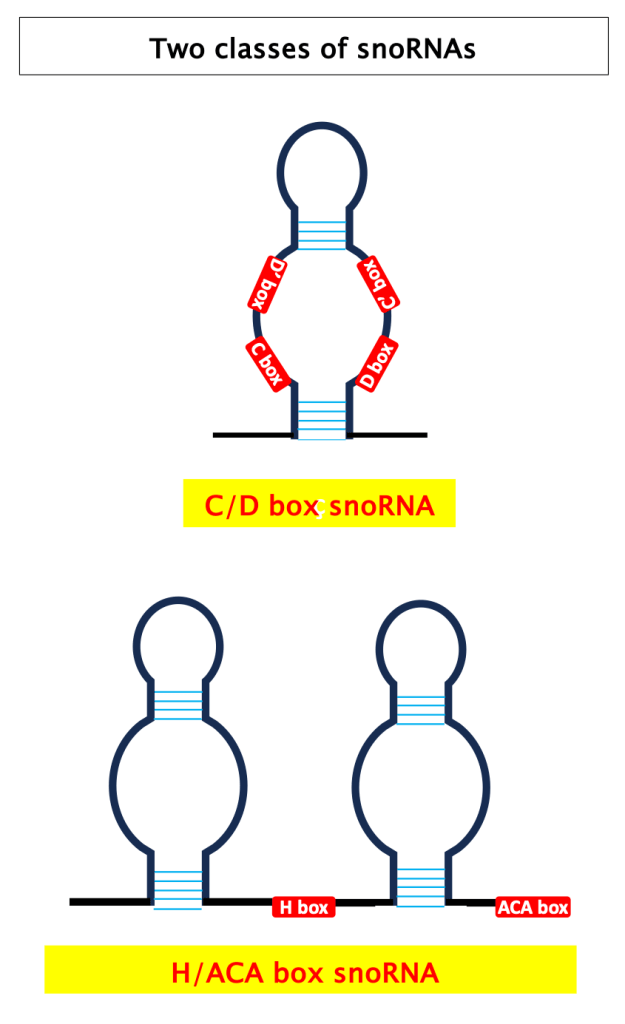
4. small nucleolar RNA (snoRNA)
They are ~60-300 nt in length, and are derived from the introns of both protein-coding and non-protein-coding genes. They localise in the nucleolus and they are essential for both rRNAs and tRNAs to properly function.
SnoRNAs assemble with specific proteins into a set of ribonucleoproteins (RNPs) responsible for the post-translation modifications of rRNAs and tRNA. SnoRNAs act as guide RNAs for RNPs to identify their targets.
SnoRNAs are divided in two classes, with distinct evolutionary conserved sequences (termed boxes): C/D box snoRNAs (~70–120 nt long) and H/ACA box snoRNAs (~100–200 nt long). A 2021 analysis identified at least 475 snoRNAs in human tissues [1, 2].
ScoRNAs can be processed into sdRNAs. In addition, they are closely related to scaRNAs.
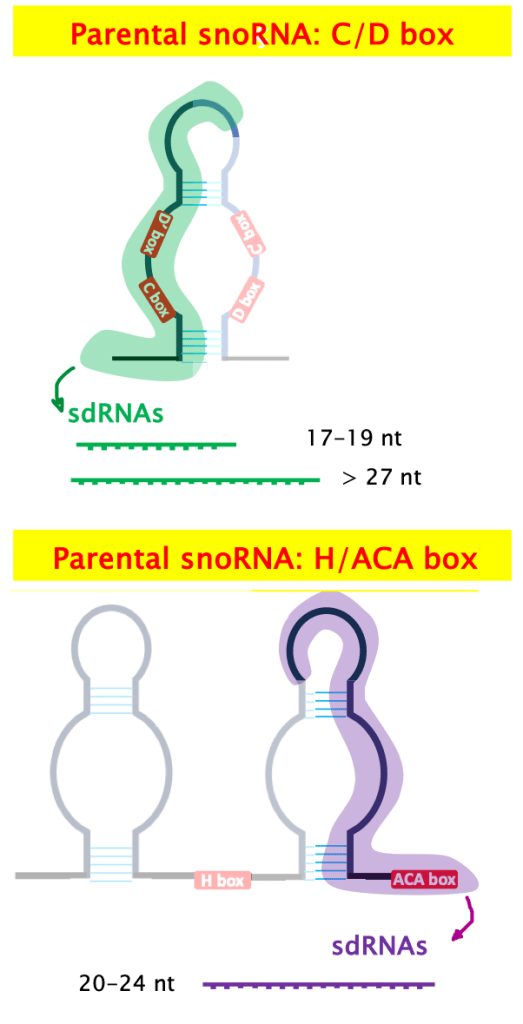
5. sno-derived RNA (sdRNA)
They are generated from cleavage of snoRNAs by the microprocessor complex (Drosha + DGCR-8), which is part of the canonical miRNA processing pathway.
Unlike snoRNAs, sdRNAs do not localise in the nucleolus but in the cytoplasm. There, they may function as miRNAs or endo-siRNAs.
The length of sdRNA depends on the parental snoRNA class: sdRNAs derived from C/D box snoRNA are 17-19 nt or over 27 nt long, while sdRNAas derived from H/ACA box snoRNA are 20-24 nt long [1].
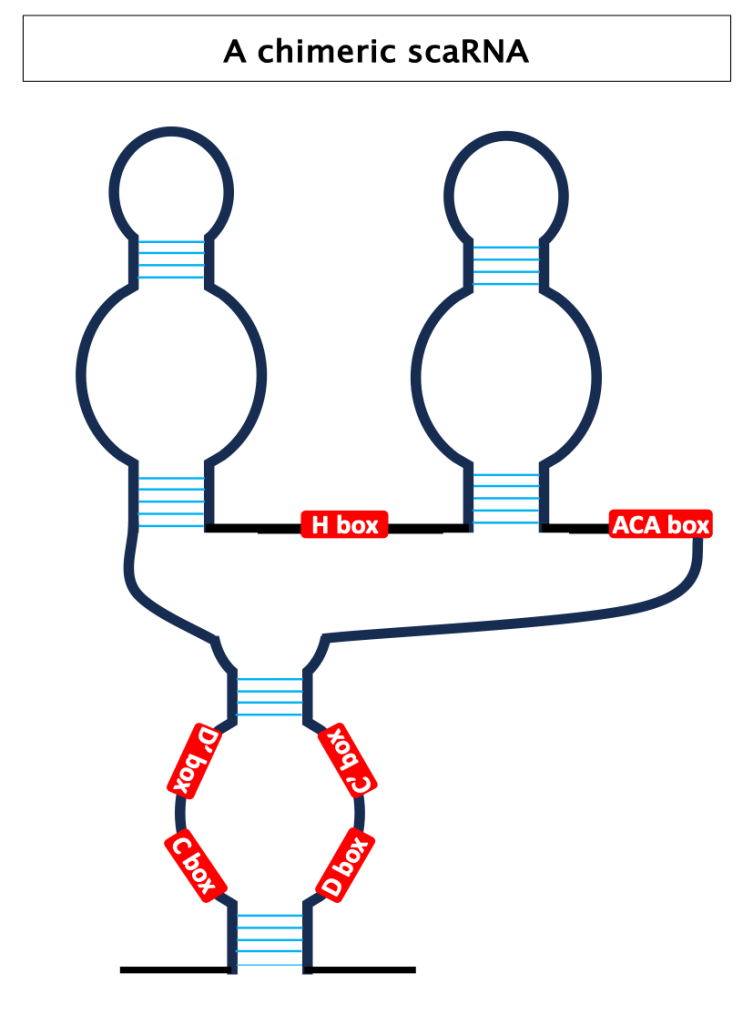
6. small Cajal body RNA (scaRNA)
They are related to snoRNAs, and localise to the Cajal bodies, a nuclear organelle. They are involved in the biogenesis of the splicing machinery and in the maintenance of the telomeres, the DNA repeats capping and protecting chromosomes.
ScaRNAs act as scaffolds on which specific proteins assemble into Cajal-body specific small ribonucleoproteins (scaRNPs). Guided to their target by their scaRNA, scaRNPs perform key modifications to the small nuclear RNAs (snRNAs) of the spliceosome [3].
In addition, a scaRNA is also part of the Telomerase, a ribonucleoprotein that elongates and maintain telomeres. The RNA part of the Telomerase (called the Telomerase RNA Component, TERC) folds into an H/ACA scaRNA [4].
ScaRNAs are classified in three groups:
- scaRNAs with C/D box sequences,
- scaRNAs with H/ACA box sequences,
- scaRNAs with C/D and H/ACA box sequences, called chimeric scaRNAs.
WHERE ARE WE GOING NEXT?
In the next episode, we pay a visit to three new types of ncRNA:
- microRNA (miRNA)
- endogenous-small interfering RNA (endo-siRNA)
- PIWI-interacting RNA (piRNA)
REFERENCES
- Taft et al. Small RNAs derived from snoRNAs (2009) RNA
- Fafard-Couture, Annotation of snoRNA abundance across human tissues reveals complex snoRNA-host gene relationships (2021) Genome Biology
- Darzacq et al. Cajal body‐specific small nuclear RNAs: a novel class of 2′‐O‐methylation and pseudouridylation guide RNAs (2002) EMBO.
- Zhang et al. Architecture of human telomerase RNA (2011). PNAS.

Leave a comment